5ACustomerJourney
5A Customer Journey
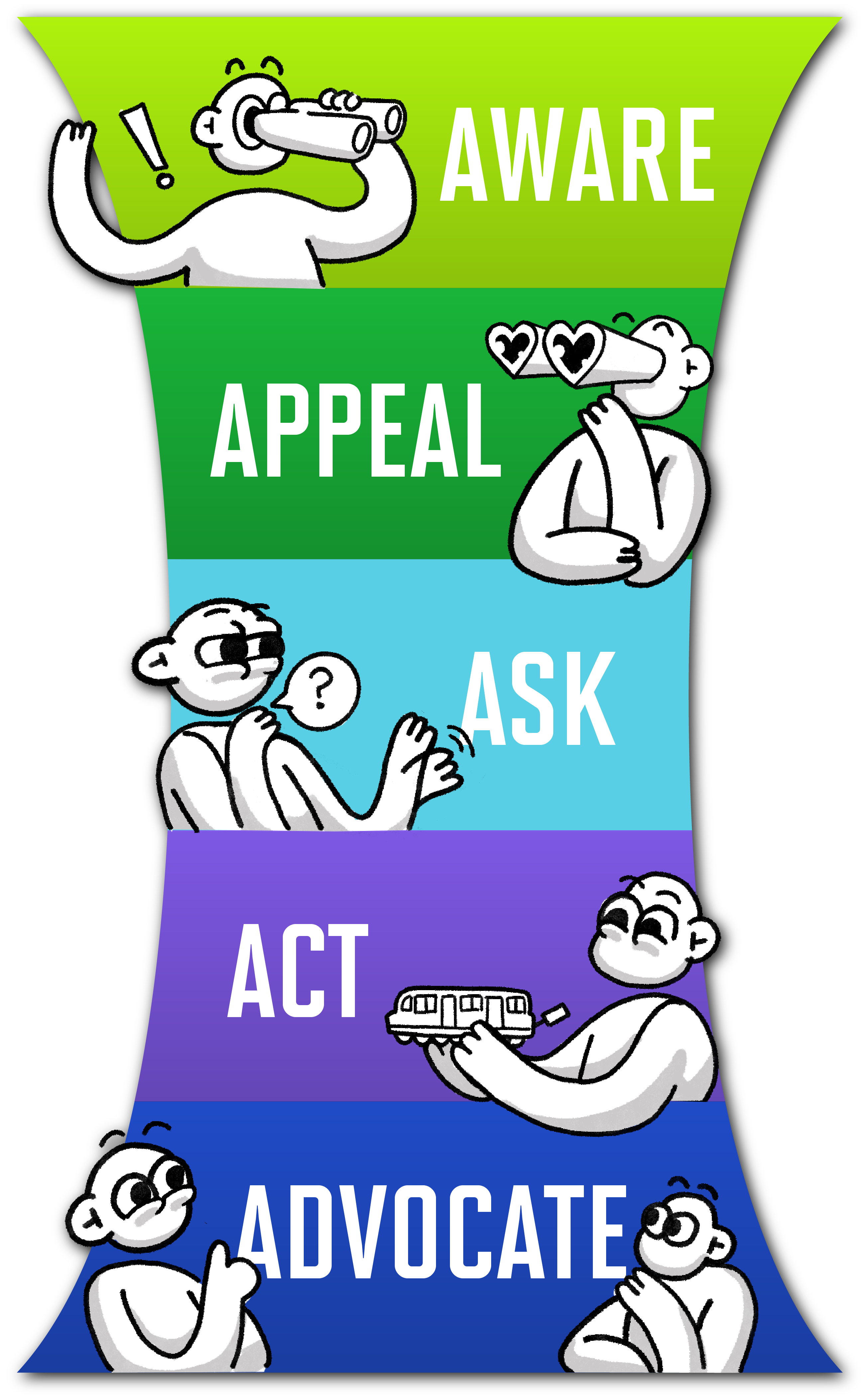
The 5A Framework—aware, appeal, ask, act, and advocate—is the modern evolution of earlier models like AIDA, reflecting today’s customer journey shaped by connectivity and social influence. Customers become aware of a brand, feel attracted to it, seek recommendations from others, make a purchase, and, if satisfied, advocate for the brand. This model highlights that customer decisions are often socially driven, and true brand loyalty is demonstrated through advocacy, not just repeat purchases.
Aware
In the aware phase, customers are passively exposed to a long list of brands through past experiences, marketing communications, and/or advocacy from others. This stage serves as the gateway to the entire customer journey. Customers with prior experience of a brand are more likely to recognize and recall it. Company-driven advertising and recommendations from other customers are key sources of brand awareness in this phase.
Appeal
After becoming aware of several brands, customers process the messages they’ve received—either forming short-term memories or reinforcing long-term ones—and become attracted to only a select few. This is the appeal phase. Brands that create a strong impression with a “wow” factor are more likely to make it onto the customer’s shortlist. In competitive and commoditized markets like consumer goods, brand appeal must be powerful, as younger generations tend to respond quickly and often act as early adopters of new products.
Ask
Driven by curiosity, customers enter the ask stage, actively seeking more information about the brands that have caught their interest—through friends, media, or directly from the brands themselves. They often look for advice, read online reviews, contact sales representatives, compare prices, or try products in-store, frequently blending both online and offline channels. Since customers draw from multiple sources, brands must maintain a strong presence across key channels.At this stage, decision- making shifts from individual to social; the brand’s appeal needs validation from others.Too little curiosity may indicate weak brand appeal, while too much can lead to confusion.
Act
If customers feel confident after the ask stage, they move to the act stage—where they take action. It's important to note that the desired customer action goes beyond just making a purchase. After buying, customers engage more deeply through consumption, usage, and after-sales service. Brands must actively involve customers and ensure a positive and memorable ownership and usage experience. When customers encounter problems or complaints, the brand must respond attentively and deliver a satisfying resolution.
Advocate
Over time, customers develop strong loyalty, reflected in retention, repeat purchases, and advocacy—this is the advocate stage. Active advocates spontaneously recommend the brand and share positive stories. However, most advocates are passive and need encouragement to voice their support. When prompted, they will defend and promote the brand. Loyal advocates also tend to make more purchases in the future, making them a valuable asset for long-term brand growth.